




Personal collective of ideas, thoughts and notes





| Languages | Javascript/Typescript |
| Frontend Frameworks | Angular, Bootstrap 4, WordPress |
| Backend Frameworks | Express |
| Build Systems | |
| Development Tools | Nodemon |
| Database | Postgres (AWS RDS) |
| Deployment | Shell scripts |
| Development | Github, VS Code, Posgres.app |
| Linting | ESLint |
| Testing | Puppeteer, Headless Chrome |
| 3rd Party | Google Services |
| Git Client | Sourcetree |
| HTTP Client | Postman |
| Source Code | Github |
| Infrastructure | Lightsail, AWS |
| Certs | Lets Encrypt |
| Domains | 1&1 |
| CLI Tools | htop, pm2, shell |
| SSH Client | Termius |
| SFTP | Filezilla |
| Monitoring | Sentry |
| AWS SES | |
| Email Templates | |
| UI Components | Envato Elements |
| Usage | Matomo |
| Marketing | ProductHunt, |
| Design | Dribbble, Adobe Behance, |
| Mockups | Sketch, Photoshop |
| Photo Editing | Photoshop |
| Vector Design/Editing | Illustrator |
| Icons | Envato Elements |
| Photos | Unsplash |
| Color Palettes | |
| Issue Management | Github Issues |
| Knowledge base | Github Wiki |
| Payment Processing | Stripe |
| Chat Support |




An ion is a atom with one of the outer electrons removed (normally removed by pointing a laser beam at it) – forming positively charged ion.
Ion trapping is done in a vacuum chamber to isolate the ions from the external environment as much as possible. (And avoid other atoms in the air from bumping and
Notes:
Quantum Systems are exponentially powerful
Based on particles: 2^500 – More particles in the universe
Challenges:
Qubit – simplest quantum system
Entanglement-
Lecture 1: Double Slit Experiment



If we add a measuring device just after the slits to track which slit the electron goes through, it “disrupts” the measurement and we get the 2nd pattern. If we use a very slight/dim light enough light, we get the 3rd “expected” pattern, but we also miss a lot of the electrons and may not capture the pattern.
= Hesienburgs uncertainty principle = Impossible to design apparatus which can detect which slit it went through without disturbing the interference pattern.
Traveling sales person problem
Solve problems which are NP hard – and they can’t be solved in polynomial time.
P versus NP problem: full polynomial versus nondeterministic polynomial problem
A P problem is one that can be solved in “polynomial time,” which means that an algorithm exists for its solution such that the number of steps in the algorithm is bounded by a polynomial function of n, where n corresponds to the length of the input for the problem. Thus, P problems are said to be easy, or tractable. A problem is called NP if its solution can be guessed and verified in polynomial time, and nondeterministic means that no particular rule is followed to make the guess.
https://www.perell.com/blog/50-ideas-that-changed-my-life
A wonderful list of principles, biases and theories which can add context, understanding and guidance through life.
http://www.paulgraham.com/ds.html#f1n
One of the most common types of advice we give at Y Combinator is to do things that don’t scale. A lot of would-be founders believe that startups either take off or don’t. You build something, make it available, and if you’ve made a better mousetrap, people beat a path to your door as promised. Or they don’t, in which case the market must not exist.
https://www.stephnass.com/blog/startup-financial-model
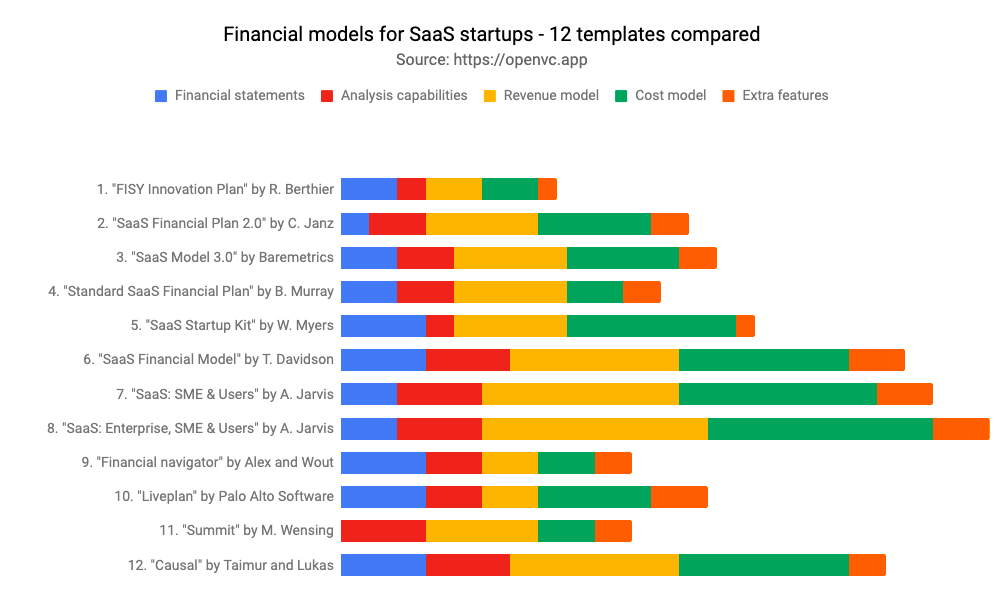
Need a financial model for your startup? Fear not. I have extensively compared the top 12 templates, free and paid, so you don’t have to do it.
You must be logged in to post a comment.