Too cheap for Strava and its “Year in Review” (Although I do miss it). so used Claude to come up with my own. Exported CSV data from Intervals.icu and imported it for analysis.
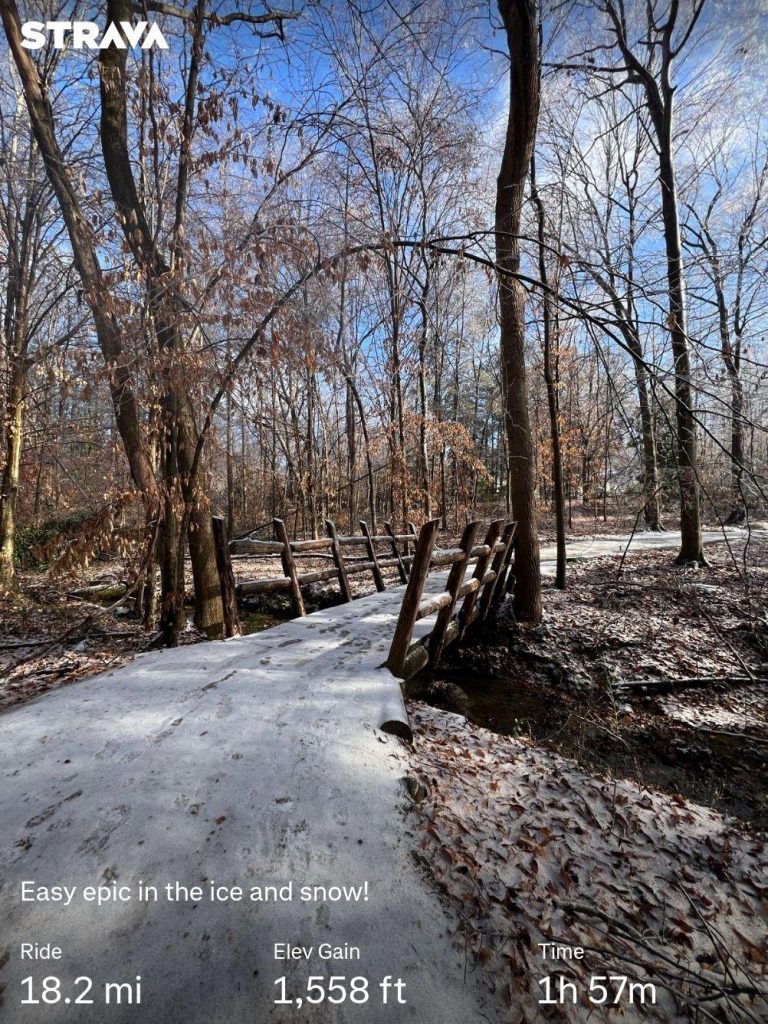
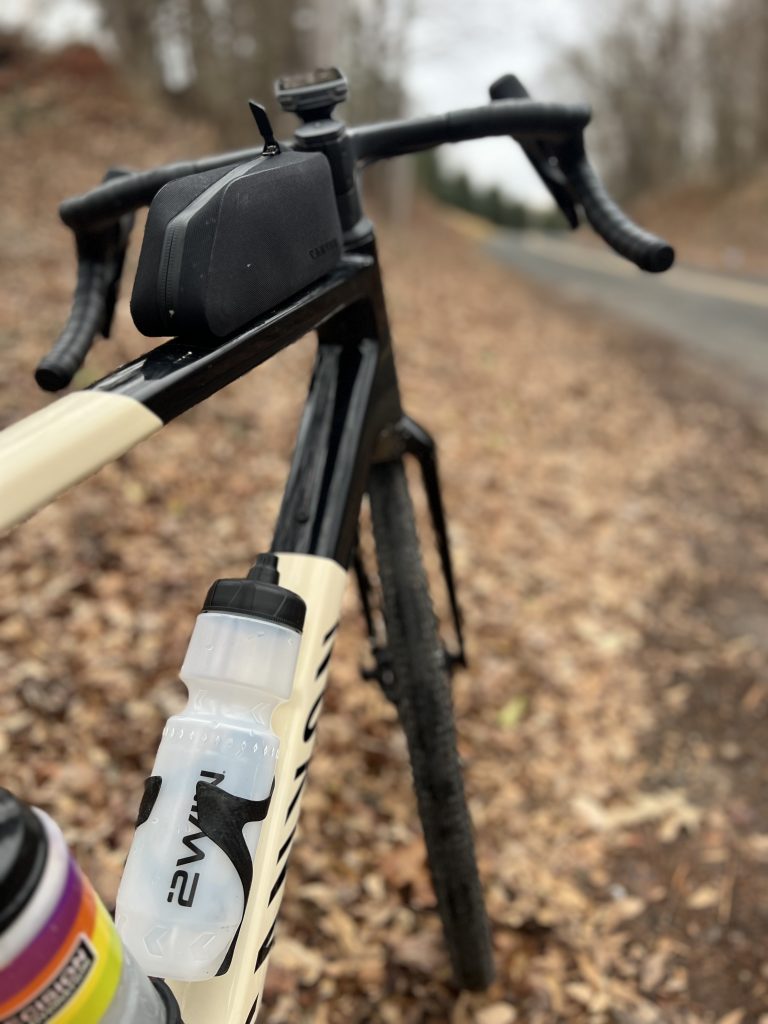
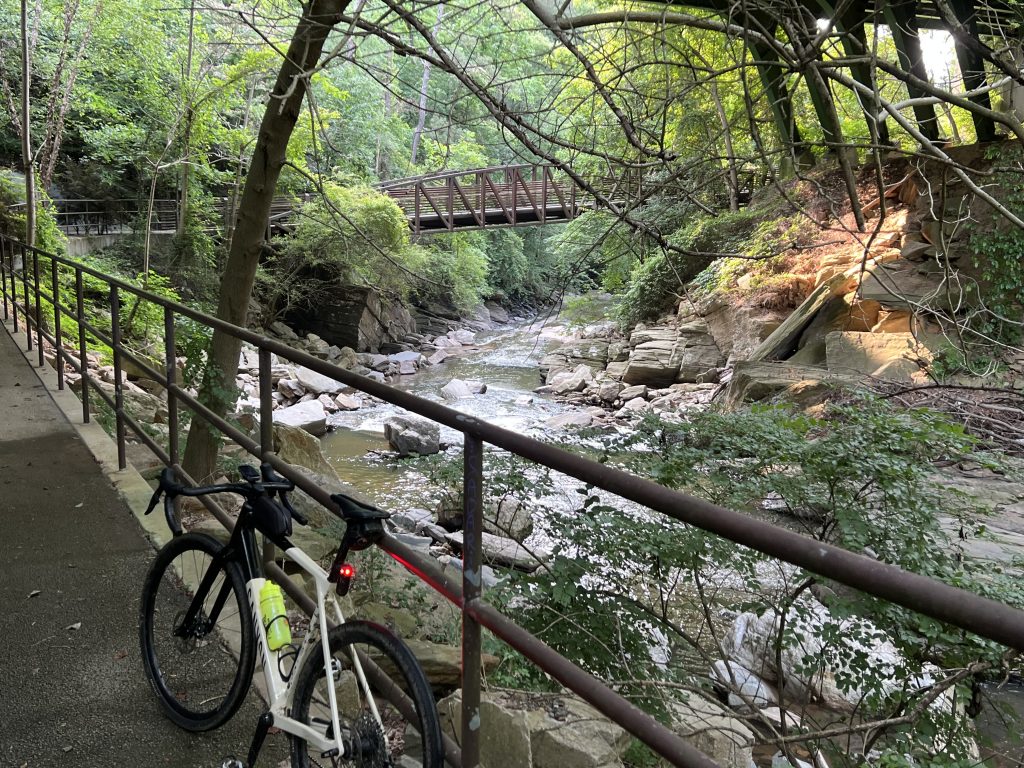
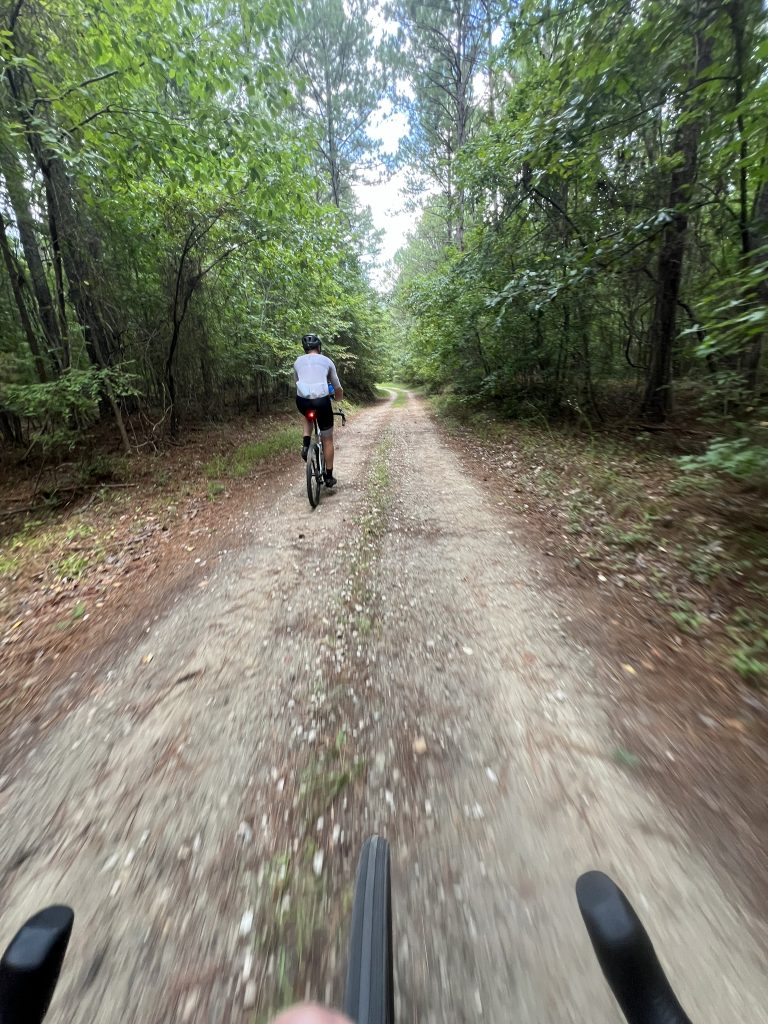
Some of my favorite workout pics from 2025








Personal collective of ideas, thoughts and notes
Too cheap for Strava and its “Year in Review” (Although I do miss it). so used Claude to come up with my own. Exported CSV data from Intervals.icu and imported it for analysis.
Some of my favorite workout pics from 2025









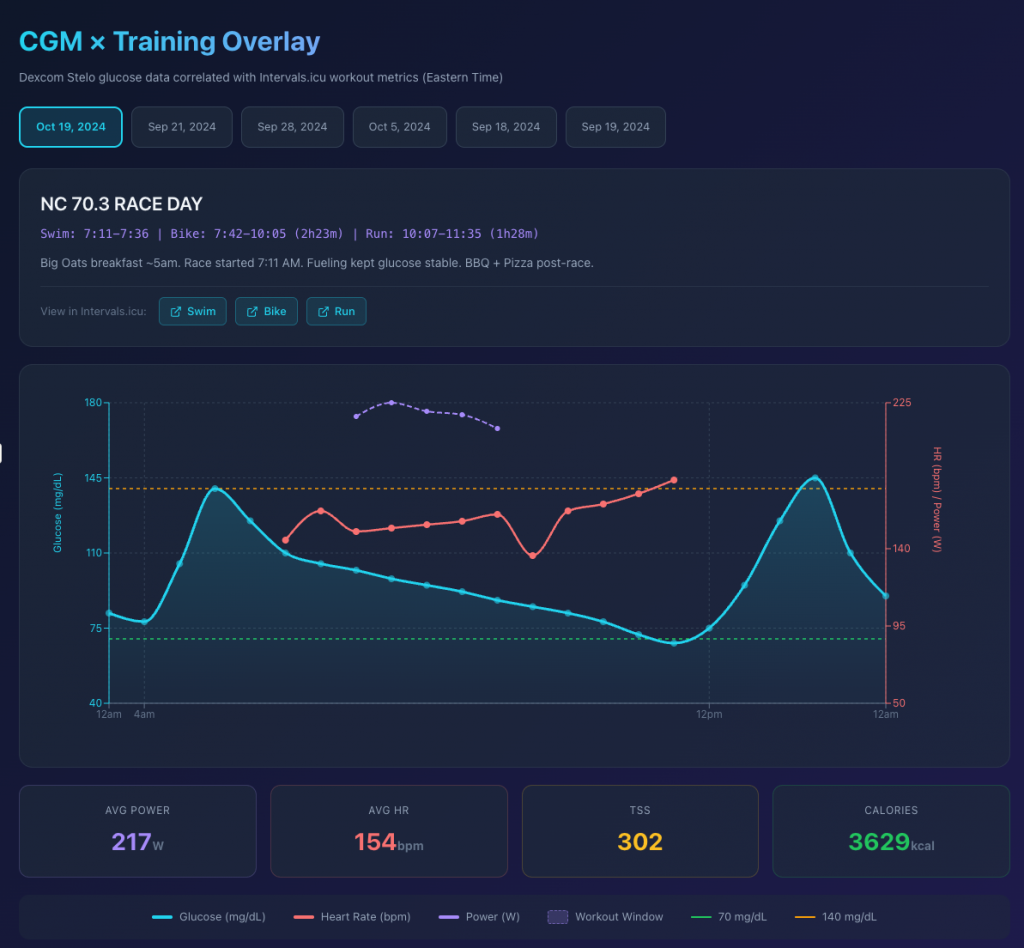
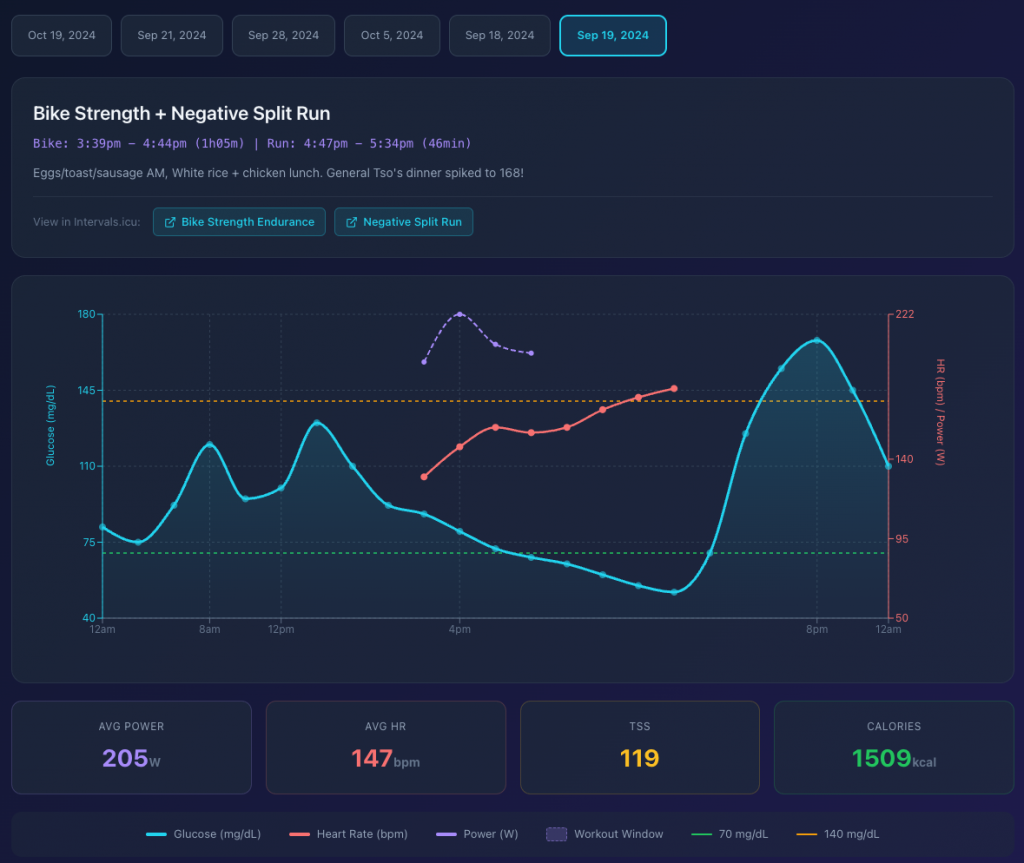
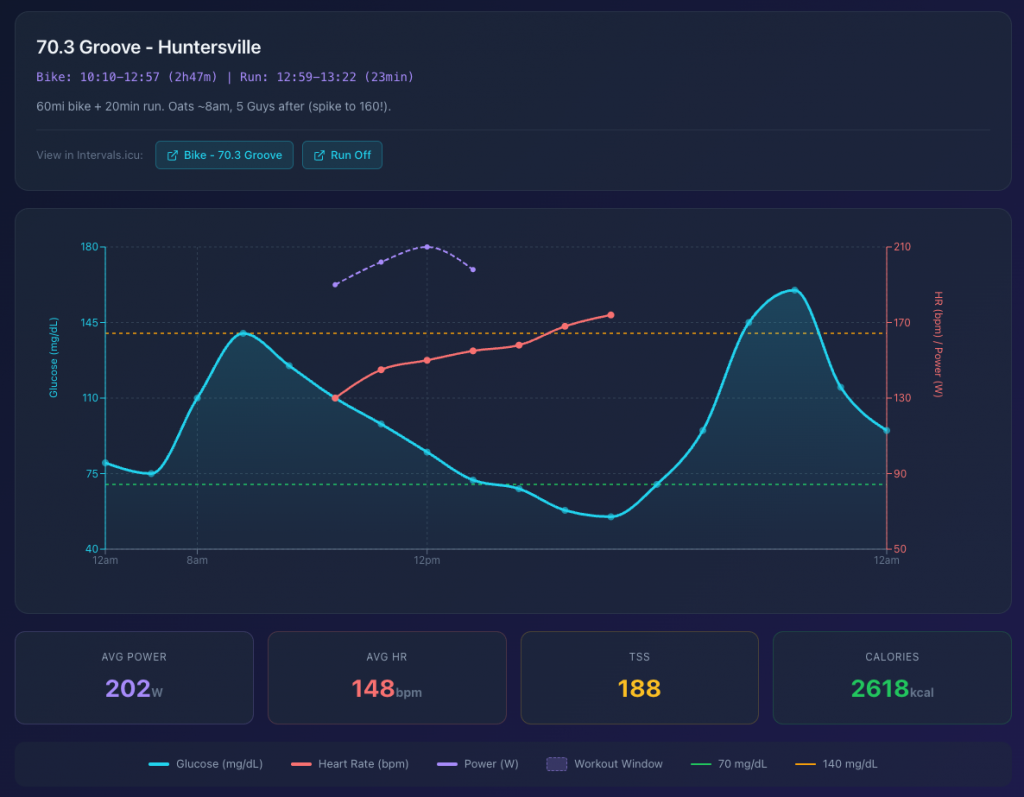
Some interesting insights from overlaying Glucose levels (from Stelo) with exercise duration/intensity.
Generated by Claude.
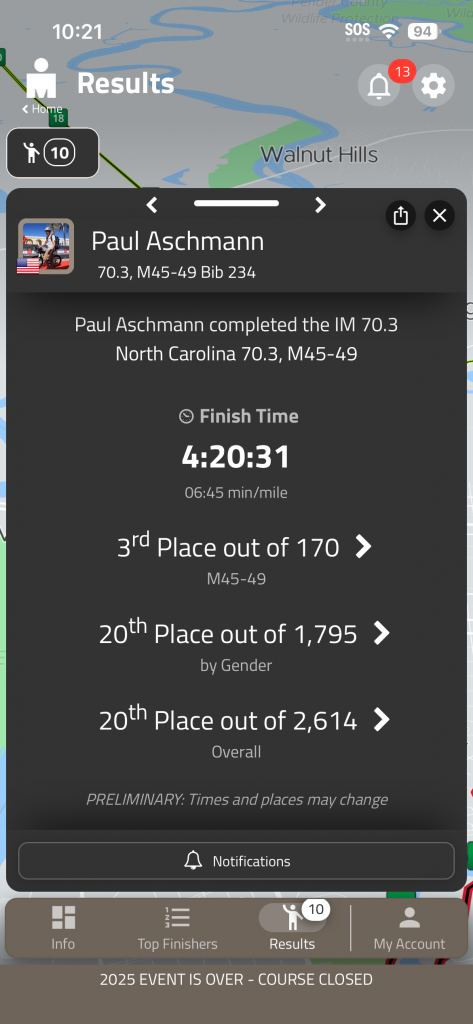
4 years in a row! A pretty solid training block going into this race despite some last minute travel to Germany for work.
| 2025 NC HIM Goal Plan vs Actuals |
|---|
| – Swim: 26:00 (Actual: 25:55, 140th OA) – T1: 5:00 (Actual: 4:30) – Bike: 2:10 (235W, 245Nor AVG < 160BPM) (Actual: 2:19, 150HR, 234W Avg, 239WNor, 18th OA) – T2: 2:00 (Actual: 1:30) – Run: 1:29 (6:35 @ 168bpm) (Actual: 1:39, 8W, 159HR, 60th OA) – Finish: 04:20:00 – Result: #3 AG, 20 OA, AG Winner 4:15?, OA Winner 3:59? |
| – Training Load: – CTL: 75 → 98 (Peak) 99 (Race) – Bike Load: 46 (Peak) 45 (Race) – Run Load: 35 (Peak) 36 (Race) – Biggest Week: 13.1 Hours, 864 TSS – Recovery Week: ~9 hours – Avg Week: ~12 hours |
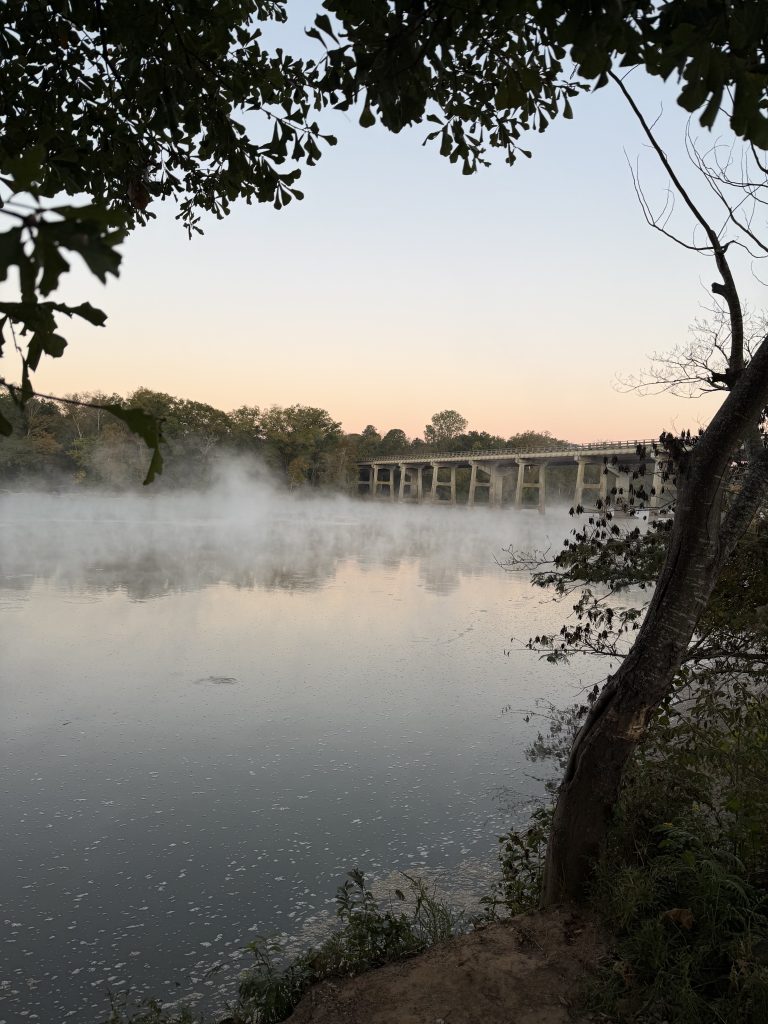
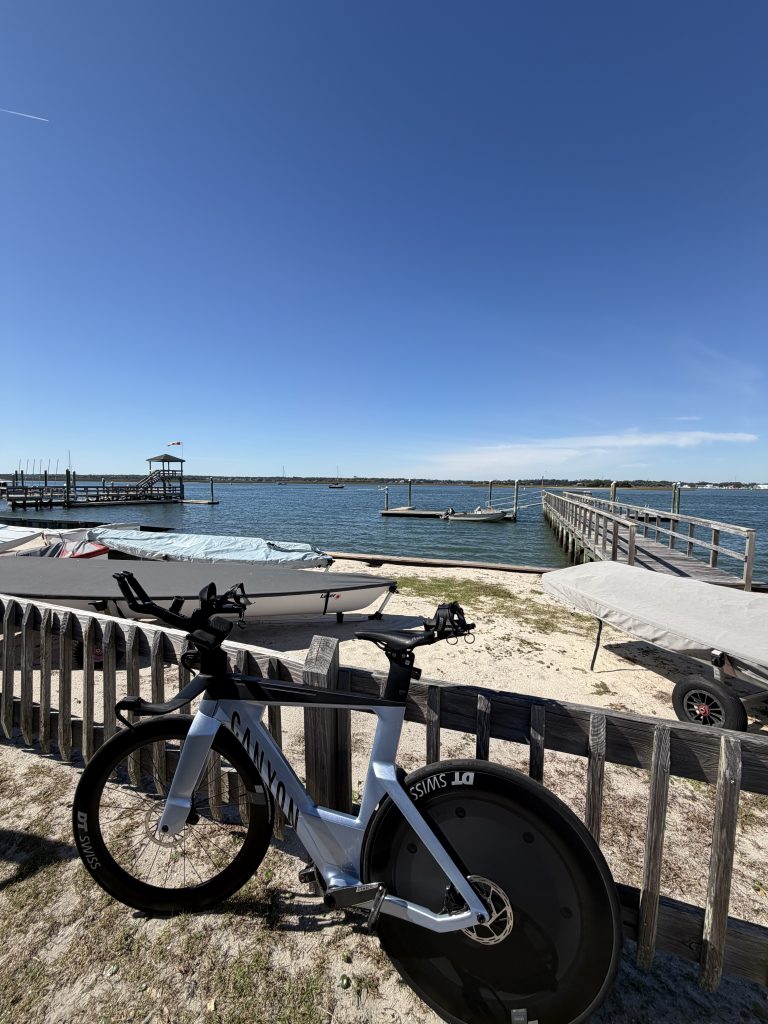
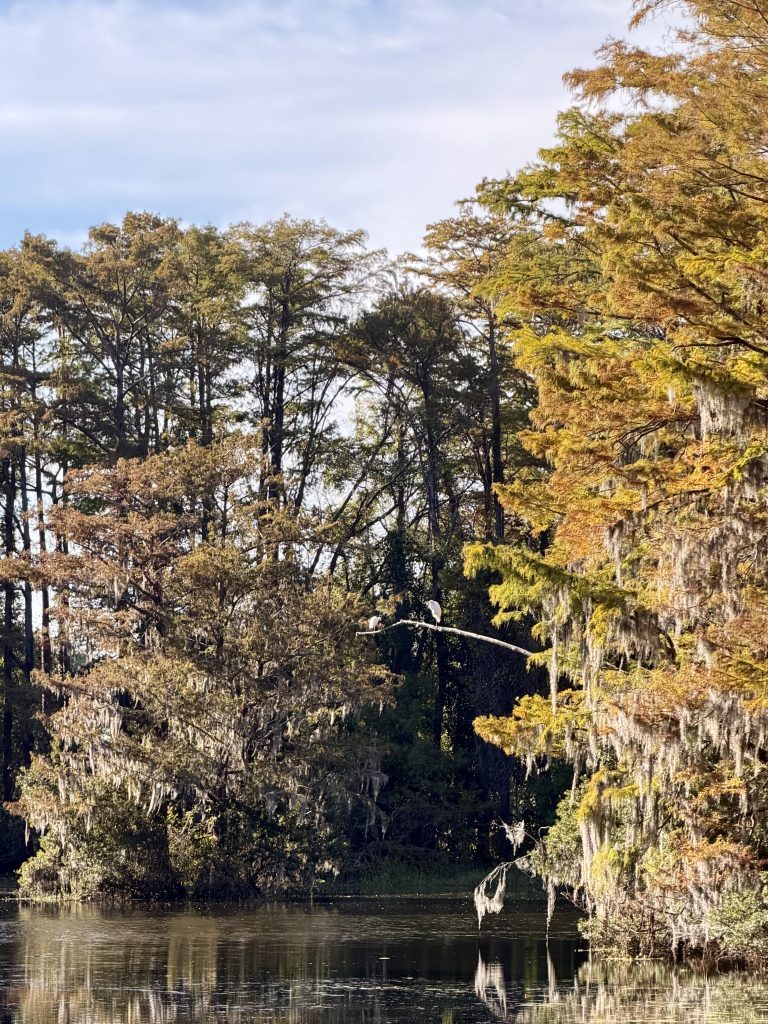
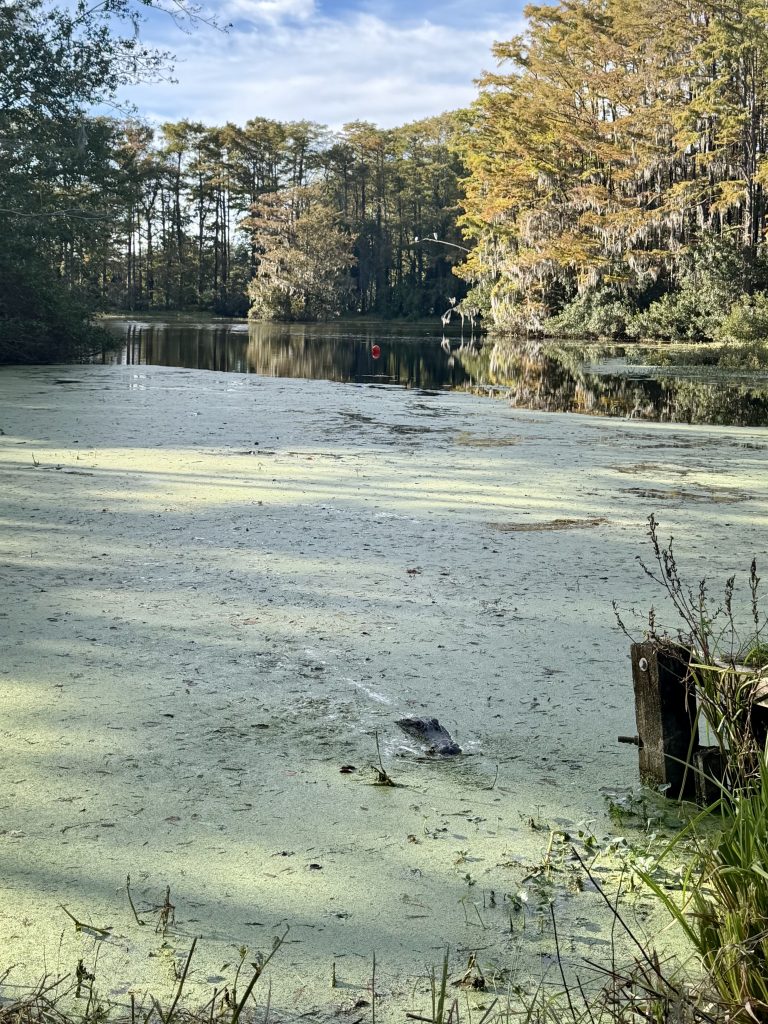
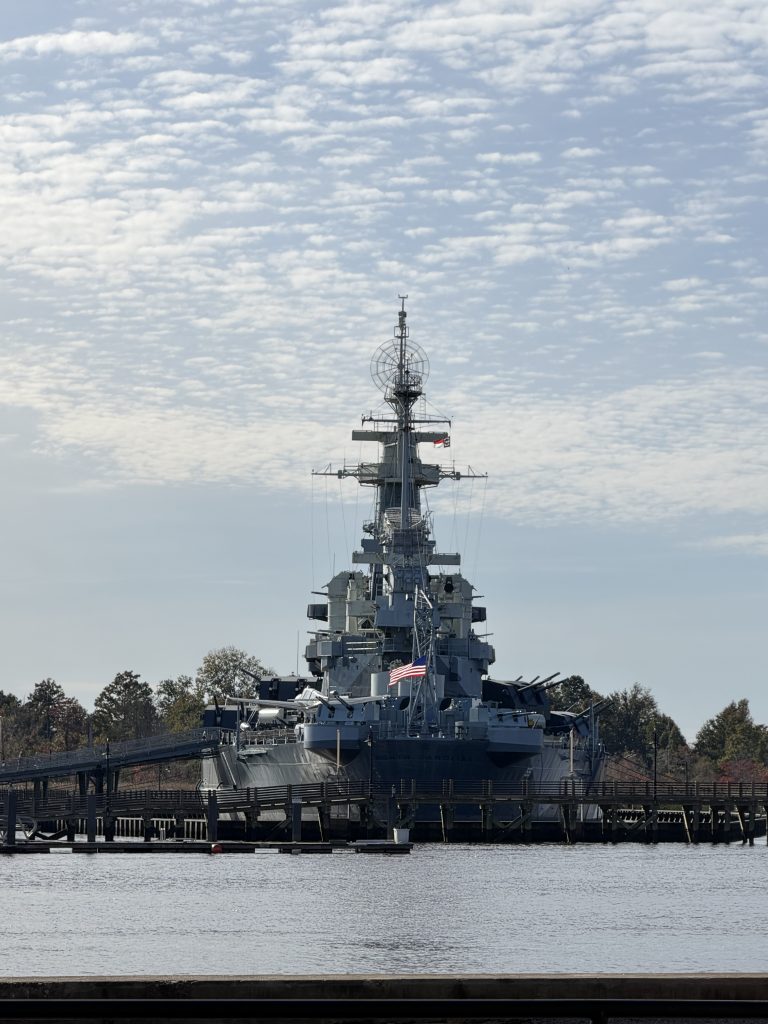












I signed up for this 2 days before the race and took advantage to get some goo open water practice in. I wasn’t quite fit enough to compete for the top spot, but considering it was at the end of a 3 week build block, I shouldn’t be surprised. I basically was only able to swim, ride and run at around 70.3 pace (and even that felt hard!). Fun day overall, great location for a race and plan to go back again next year!
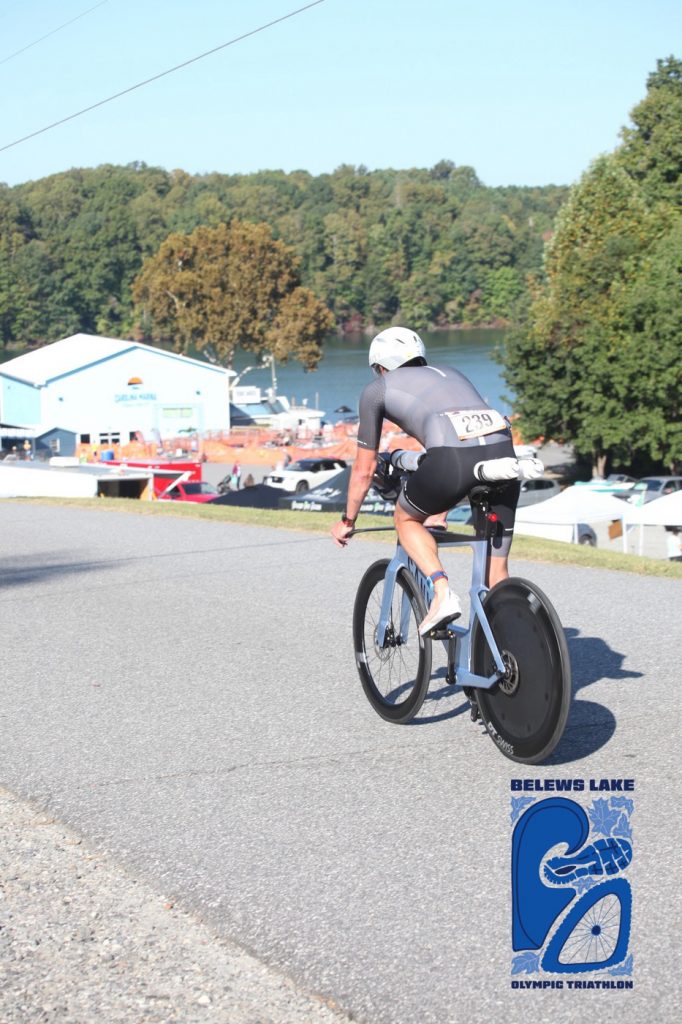
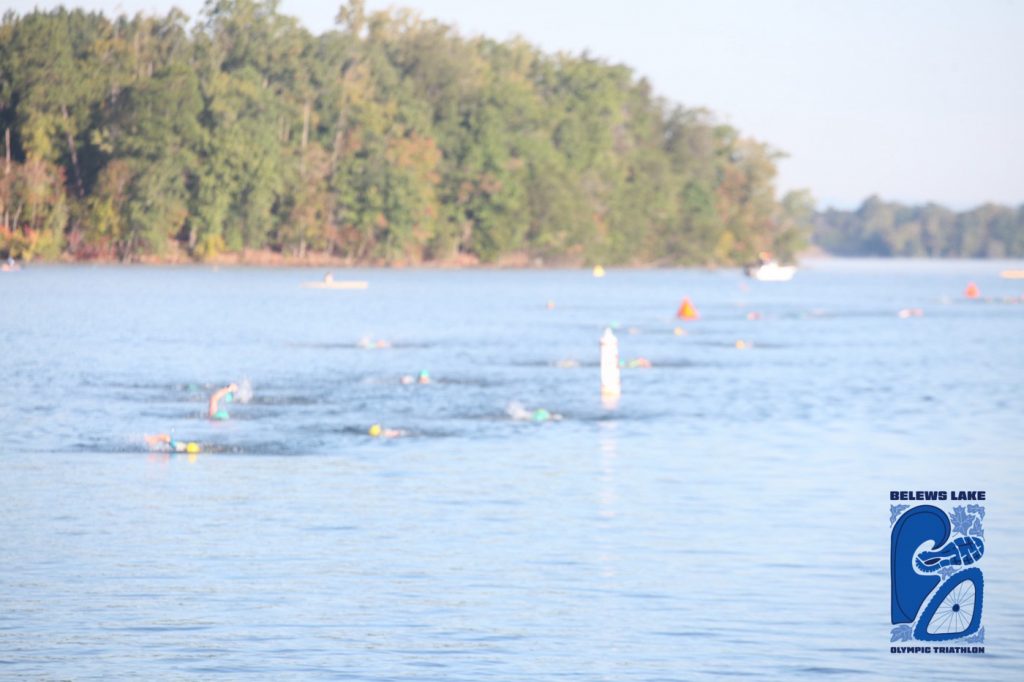
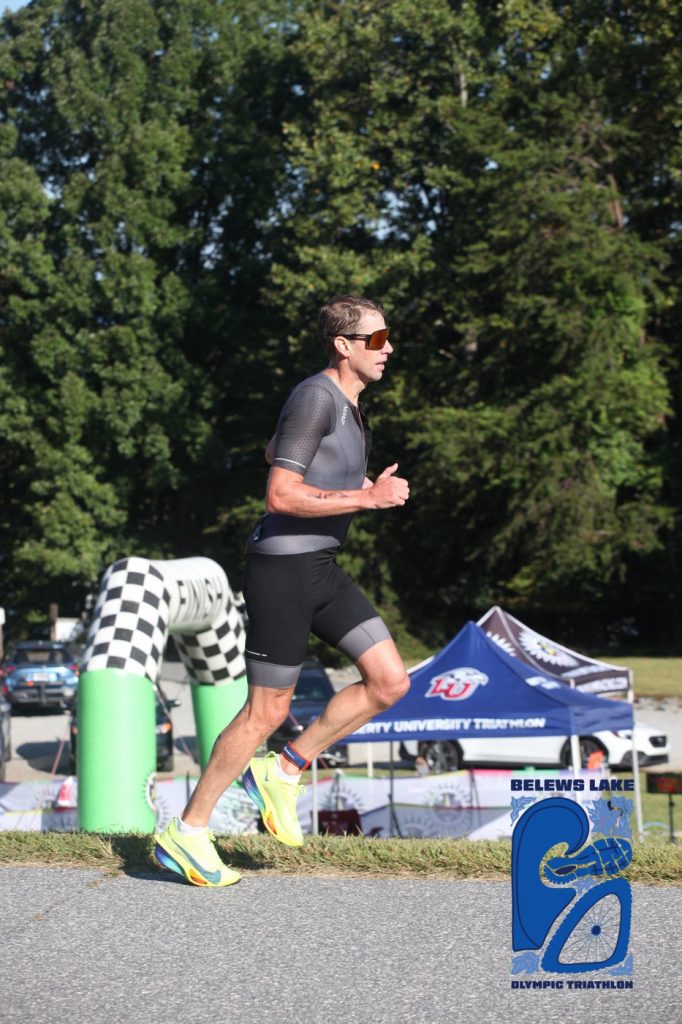
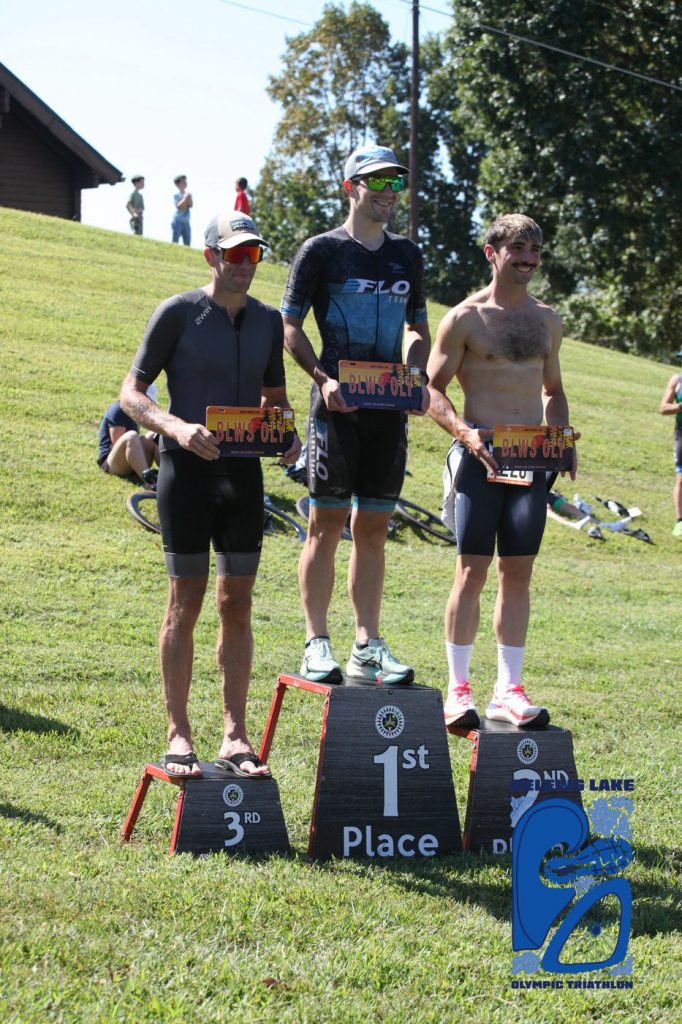






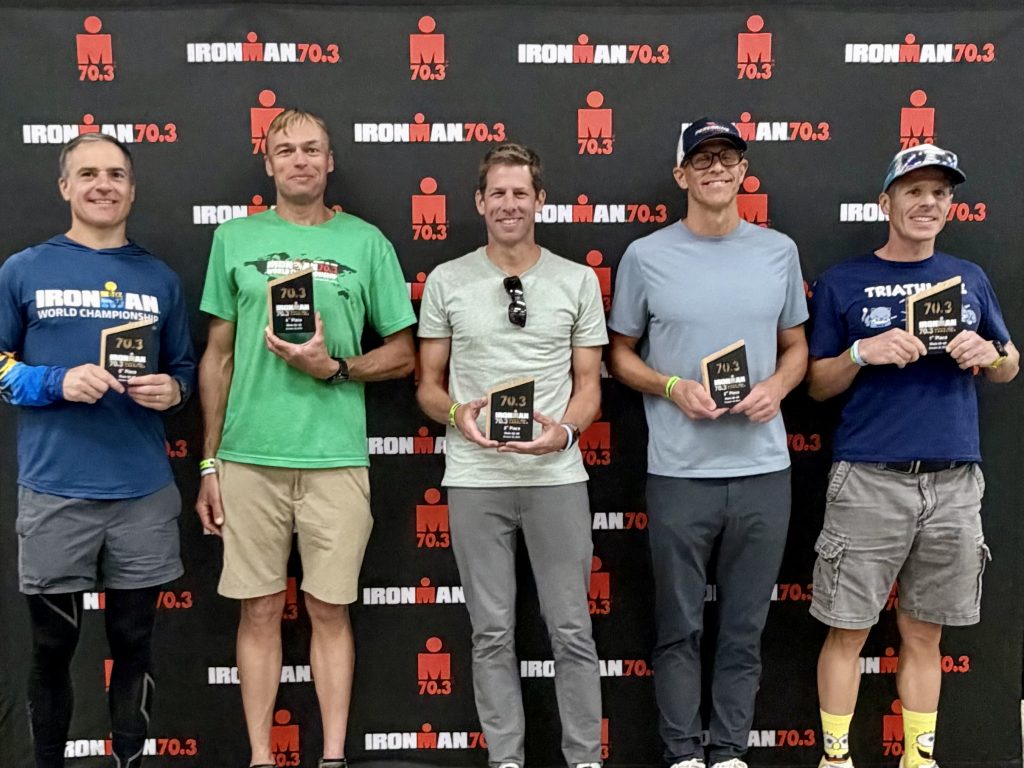
Another Ironman 70.3 race under my belt and my best overall finish to date! It was slightly disappointing that the swim was cancelled due to strong currents, but if its the same for everyone, that works for me 🙂
The race venue, people and weather were perfect. Aside from my very first 70.3 in Augusta, I think this has been my favorite. This was probably influenced by some personal bests on all fronts, however, with not having a swim, I think that could have been expected to a small extent.
The weekend started by taking a beautiful drive up to Chattanooga through the mountains on Thursday, I left early so I could get work in once I arrived and avoid some traffic. The drive alone is worth the trip, along the beautiful Nantahala river through towns like Asheville and Bryson City.
While prepping my bike for Leadville, I completely screwed up and managed to strip the hex head of the shock mount bolt. I subsequently used an easy out to get some grip on the bolt and start applying some rotational torque. In doing so, I missed the fact the bolt could be seized in the shock bushing 🙁 So while I thought I turning the bolt out, I was implying “pushing” the back of the shock stay outward, and it cracked the frame 🙁
Sweating I reached out to Canyon, explained the situation, and they kindly warranted it! Part of the claim process was to destroy the old frame so after ~ 4,814 miles, it’s gone in the trash can. Some good memories on this bike for sure!
I am a marketers dream and loyalty programs were invented for me 🤣 … fun to have some small recognition as a AWA Gold Athlete in 2024/2025 again.


Finally outside after speeding the first couple hundred miles on the trainer 🙂








Another fun year chasing some kudos and KOM’s on #Strava!






You must be logged in to post a comment.